B. Gross Findings:
-
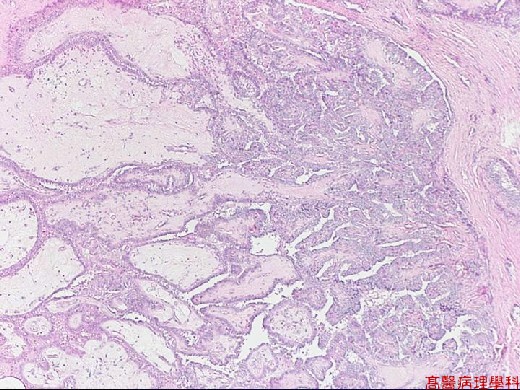
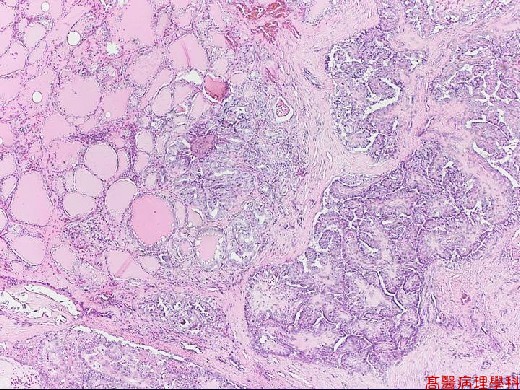
Solid, firm, grayish white lobulated lesion with sclerotic center.
C. Micro Findings:
-
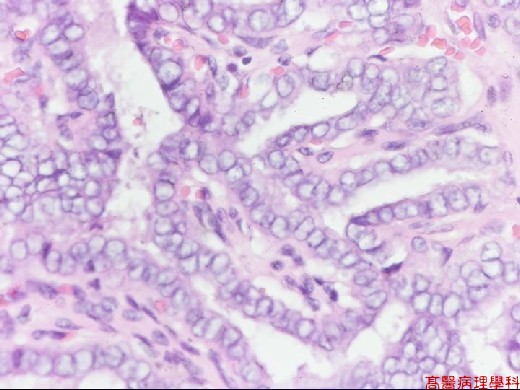
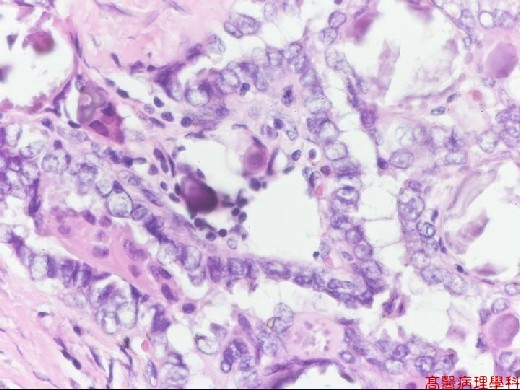
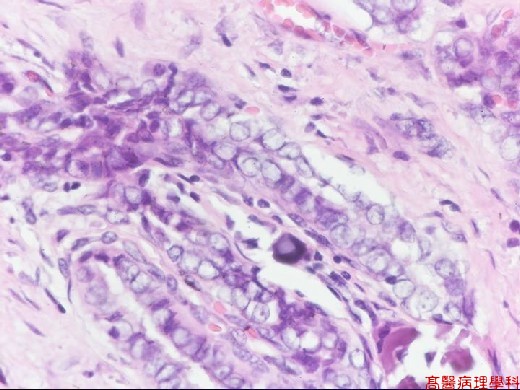
Based on characteristic architecture & cytological feature.
-
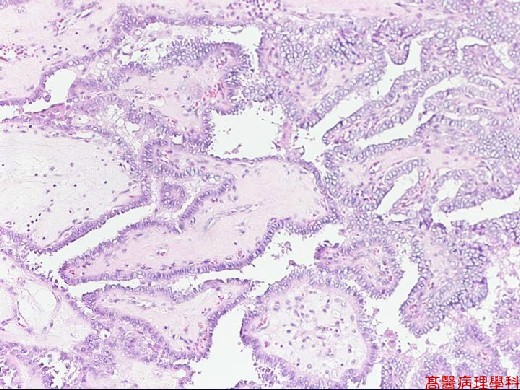
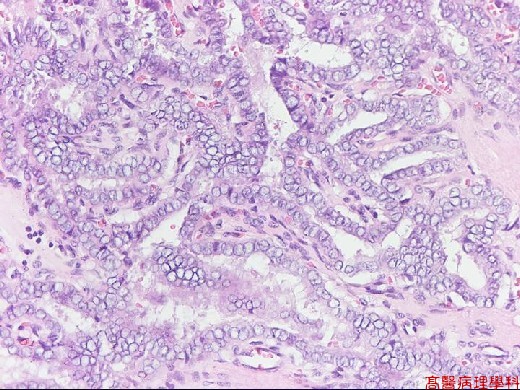
Papillae formed by a central fibrovascular stalk & covered by neoplastic epithelial cells.
-
Psammoma bodies in the papillary stalk, fibrous stroma or between tumor cells.
-
Nuclear features:
-
Round to slight oval shape.
-
Pale, clear, empty or ground glass appearance (Orphan Annie): empty of nucleus with irregular thickened inner aspect of nuclear membrane.
-
Pseudo-inclusion: deep cytoplasmic invagination and result in nuclear acidophilic, inclusion-like round structures, sharply outlined and eccentric, with a crescent-shaped rim of compressed chromatin on the side.
-
Grooves: coffee-bean like.
-
D. Others:
-
The most common form of differentiated thyroid carcinoma.
E. Reference:
-
Robbins Pathologic Basis of Disease, 6th ed. P.1143.
|
|
【 Fig. 92-1 (10X)】
|
|
【 Fig. 92-2 (4X)】
|
|
【 Fig. 92-3 (10X)】
|
|
【 Fig. 92-4 (20X)】
|
|
【 Fig. 92-5 (40X)】
|
|
【 Fig. 92-6 (40X)】
|
|
【 Fig. 92-7 (40X)】