《Slide 21.》Postnecrotic Cirrhosis, Liver
A. Brief Descriptions:
-
Cause : alcohol abuse , chronic hepatitis , biliary disease and iron overload.
-
Progressive fibrosis of liver parenchyma.
-
It is generally irreversible.
B. Gross Findings:
-
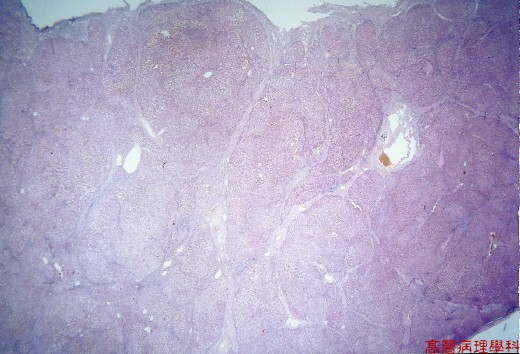
Macronodular cirrhosis with marked variation in size & shape of the nodules ( 3mm - 10mm or larger ).
C. Micro Findings:
-
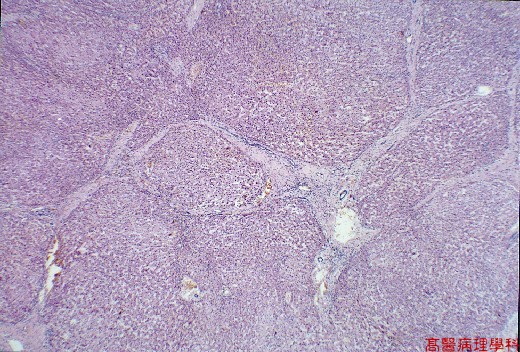
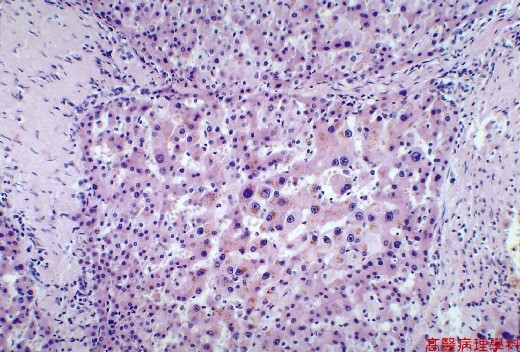
Fibrosis, regenerated nodules & complete vascular/microanatomical distortion.
-
Thick or thin fibrous septi with venous radicals, bile ducts, & arteries without normal portal tracts.
D. Others:
1. Classified by its etiology.
2. The end stages of almost any form of chronic active liver disease.
3. Def. of cirrhosis:
l A diffuse process characterized by fibrosis & a conversion of normal architecture into structurally abnormal nodules.
l A chronic irreversible disease of liver in which the normal architecture is destroyed by deposition of connective tissue & regenerated nodules.
E. Reference:
-
Robbins Pathologic Basis of Disease, 6th ed. P.853-855.
|
|
【 Fig. 21-1 (LP)】
|
|
【 Fig. 21-2 (LP)】
|
|
【 Fig. 21-3 (HP)】