《Slide 40.》Intestinal tuberculosis, Intestine
A. Brief Descriptions:
-
Usually located in the ileocecal area.
B. Gross Findings:
-
Following the localization of lymphoid tissue in small bowel.
-
Annular ulcers lying transversely & raised above mucosa, sometimes with stricture.
-
Local lymph nodes enlarged with florid caseating granuloma.
-
Cut surface: white & friable.
C. Micro Findings:
-
Large, closely packed granuloma, common in Payer’s patches.
-
Caseating foci, surrounded by epithelioid cells, Langhans` giant cells, lymphocytes & peripheral fibrosis.
-
Langhans` giant cells: nuclei ring surrounding in eosinophilic cytoplasm.
D. Others:
-
Mycobacterium tuberculum
-
0.2-0.5 by 2-5 um, straight or curved rod.
-
Proved by culture, acid fast stain, or hybridization.
-
Forms:
-
Primary: infected the mesenteric lymph nodes & bowel walls.
-
Secondary: swallowed sputum from an existing pulmonary lesion.
E. Reference:
-
Robbins Pathologic Basis of Disease, 6th ed. P.349-352.
|
|
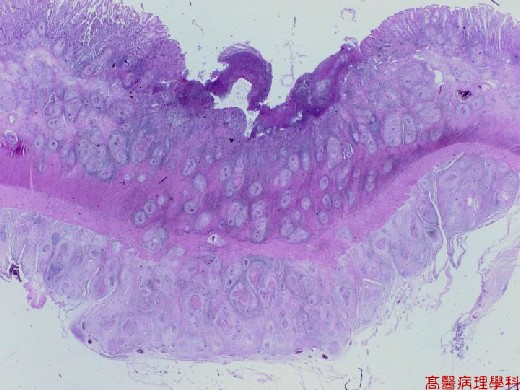
【 Fig. 40-1 (LP)】Ulceration of the colonic mucosa with numerous transmural nodules infiltrate.
|
|
【 Fig. 40-2 (LP)】Presence of nodules in mucosa (top) and submucosa (top).
|
|
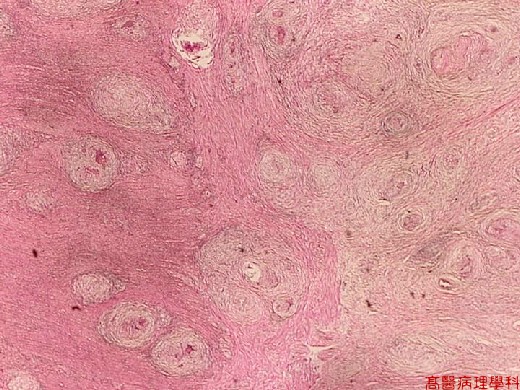
【 Fig. 40-3 (LP)】Numerous nodules infiltrate in muscularis propria (left) with extension to serosa (right).
|
|
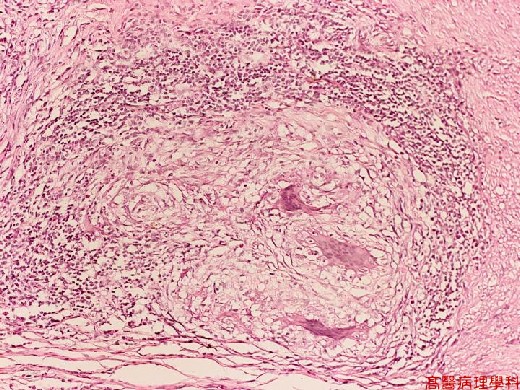
【 Fig. 40-4 (HP)】The nodule (tubercle, caseous granuloma) is composed of caseous necrotic debris in the center, infiltrated by epithelioid histiocytes and surrounded by lymphocytes at peripheral. Note Langhans’ giant cells.