B. Gross Findings:
-
Tangle network of numerous、worm-like、abnormally tortuous misshapen vascular channels.
C. Micro Findings:
-
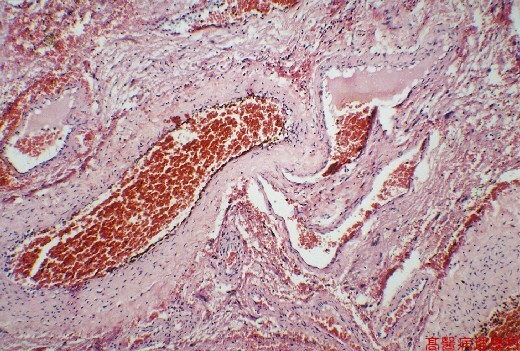
Tangles of abnormal vessels of various diameter seperated by gliotic tissue in the absence of intervening capillary bed often with evidence of prior hemorrhage.
-
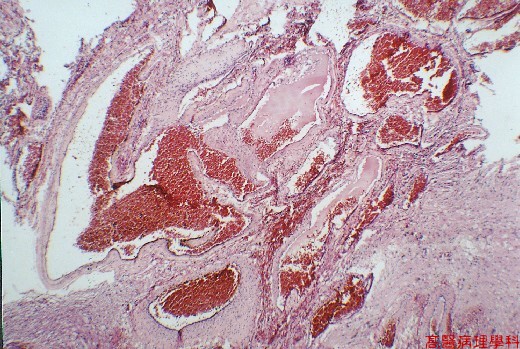
Some vessels have the thin collagenous walls of veins,whereas others the muscular and elastic laminae of arteries or structural hybrids.
-
Artery feeding a vein.
-
Arterialization of vein: abnormally thick-walled veins.
-
Elastic stains identify arteries and focal loss or duplication of elastin.
-
Crescents of mural calcification may outline the contours of some vessels.
-
Variable gliosis or hemosiderin-stained interposed brain parenchyma.
-
Congestion of the vessels、thrombi.
-
Perivascular inflammation.
D. Others:
-
病理組織重點:
-
Abnormal communication between arteries and veins.
-
Absence of intervening capillary bed.
-
E. Reference:
-
Robbins Pathologic Basis of Disease, 6th ed. P.1313.
|
|
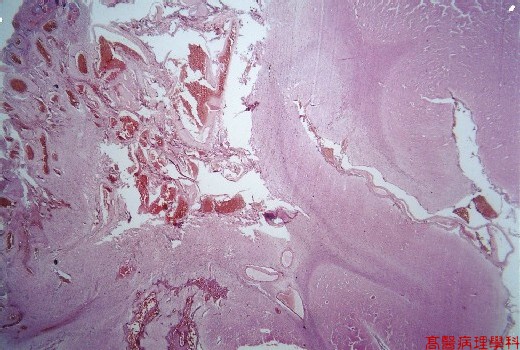
【 Fig. 49-1 (LP)】Proliferation of variant sized blood vessels (left) in the surface of brain; note cerebral parenchyma in the right.
|
|
【 Fig. 49-2 (LP)】Tangles of abnormal vessels of various diameter, some vessels have the thin collagenous walls of veins, whereas others the muscular and elastic laminae of arteries or structural hybrids.
|
|
【 Fig. 49-3 (HP)】Thick and thin walled vessels without intervening capillary bed.