B. Gross Findings:
-
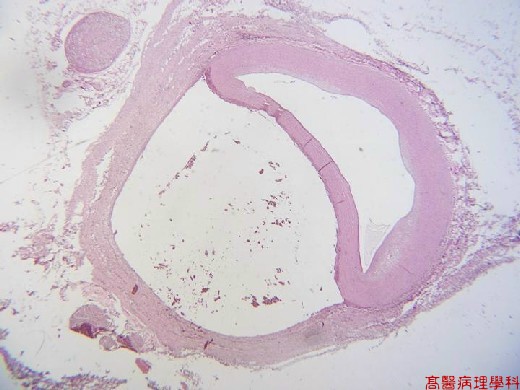
Dissection of blood vessel along the laminar planes of arterial media with the formation of a blood-filled channel.
C. Micro Findings:
-
Dissection between middle and outer thirds of tunica media with the formation of two lumens (Medial splitting by hemorrhage;usually associated with elastic fragmentation and fibrosis).
-
true lumen :endotheial-lining wall, smooth.
-
false lumen: RBC-coating wall, irregular.
-
D. Others:
略.
E. Reference:
-
Robbins Pathologic Basis of Disease, 6th ed. P.525.
|
|
【 Fig. 50-1 (LP)】Dissecting aorta with two lumens: true lumen in the right, while false lumen in the left; note nerve ganglion in the periaortic soft tissue (left).
|
|
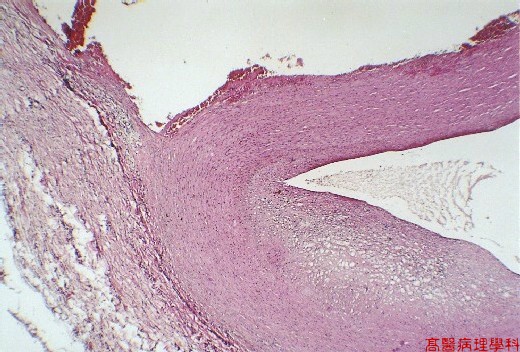
【 Fig. 50-2 (LP)】False lumen (upper) with irregular surface and blood clots, while true lumen (low) with endothelial lining; note atherosclerotic change in the wall (right lower).
|
|
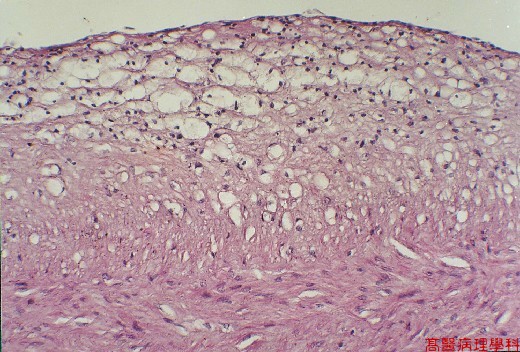
【 Fig. 50-3 (HP)】Detail of atherosclerotic change of wall with cholesterol-laden macrophages (foamy histiocytes).