《Slide 114.》Central necrosis , Liver
A. Brief Descriptions:
-
Right-sided cardiac failure→ passive congestion of the liver→congestion of centrilobular sinusoid→ centrilobular hepatocytes become atrophic.
-
Left-sided cardiac failure→ hepatic hypoperfusion→centrilobular necrosis.
-
Centrilobular hemorrhagic necrosis; nutmeg liver.
B. Gross Findings:
略.
C. Micro Findings:
-
Central area show necrosis with slight inflammation.
-
Preserved periportal area.
D. Others:
-
Compare with slide 24. Cardiac congestion of liver and slide 121. Cardiac cirrhosis of liver.
E. Reference:
-
Robbins Pathologic Basis of Disease, 6th ed. P.882~883.
|
|
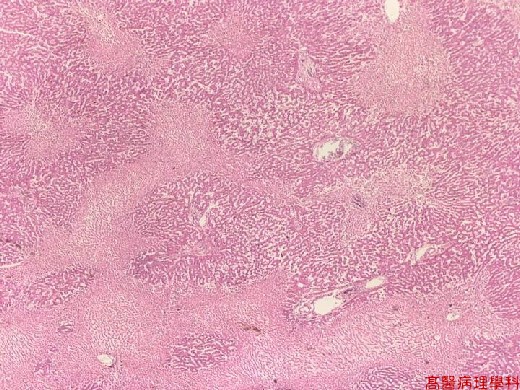
【 Fig. 114-1 (LP)】Sharp demarcation between necrotic and viable area.
Necrosis (left lower) is around the centrilobular area. The periportal area is viable.
|
|
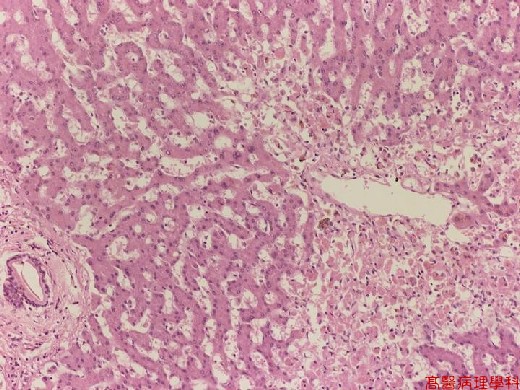
【 Fig. 114-2 (LP)】Congestion and coagulative necrosis of the centrilobular area (left). Inflammation is mild.
|
|
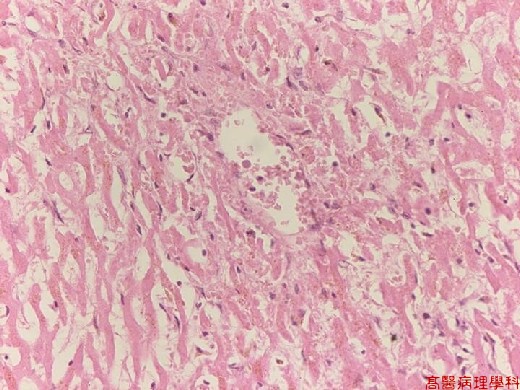
【 Fig. 114-3 (HP)】Ischemia of centrilobular area resulting in coagulative necrosis of hepatic cords. (Preservation of cellular contour with disappearance of nucleus) Some viable hepatocytes with nucleus are seen in the upper middle and upper right areas.