《Slide 135.》Intradermal nevus, Skin
A. Brief Descriptions:
-
Congenital or acquired.
-
Tan to brown, uniformly pigmented, small solid lesion of flat to elevated skin.
B. Gross Findings:
-
Papillary, pedunculated, dome shaped or flat, with or without hairs, brown or little darker than surrounding skin.
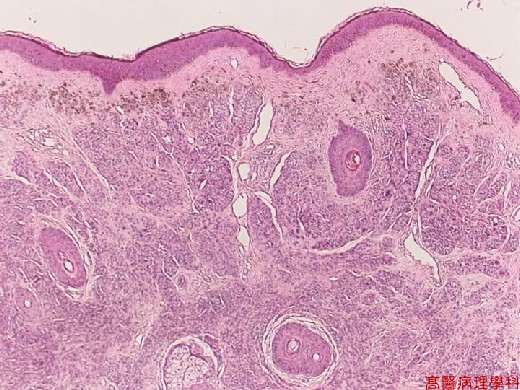
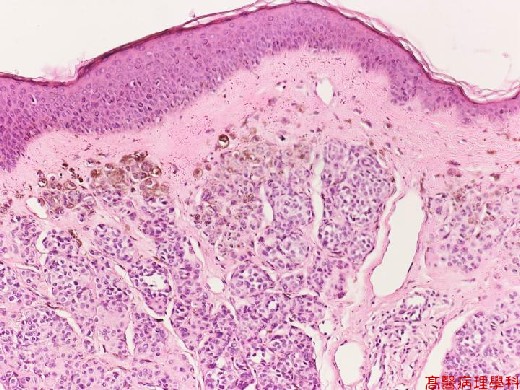
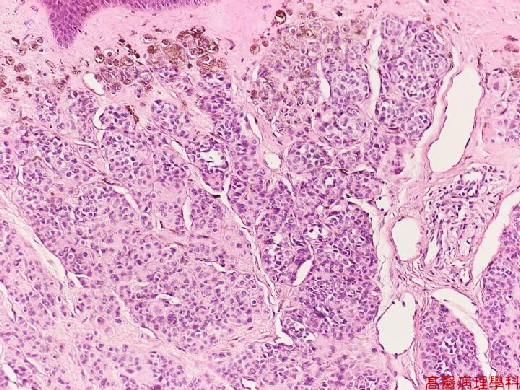
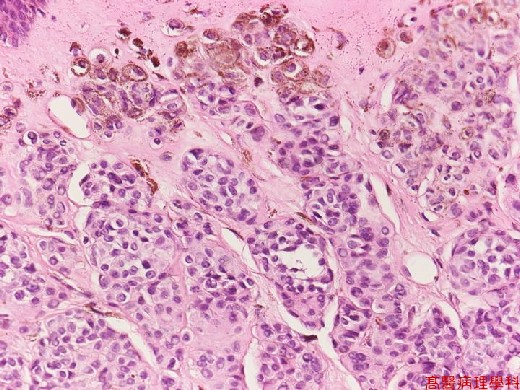
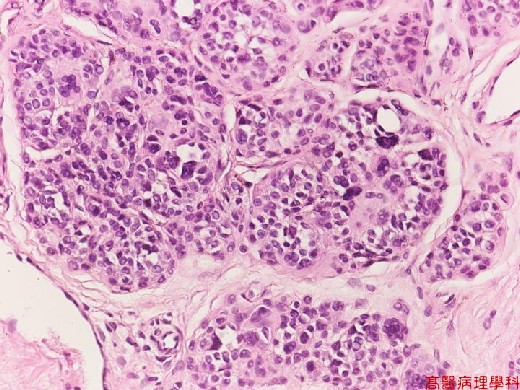
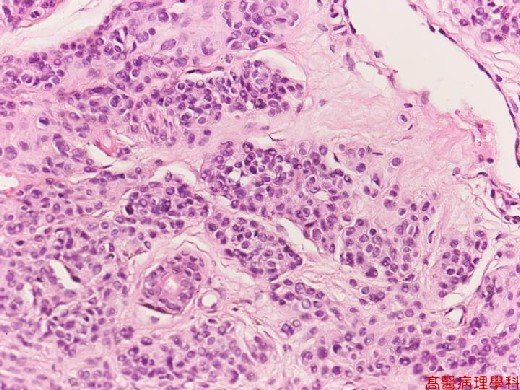
C. Micro Findings:
-
Small nests or bundles of nevus cells in dermis with thinned overlying epidermis.
-
Nevus cells: (no necessarity to differentiate these cells described below).
-
Cuboidal cells with regular, spheroid, moderately hyperchromatic nuclei.
-
Upper: larger cells (type A) with some multinucleated giant melanocytes.
-
Middle: smaller cells (type B) like lymphocytes.
-
Lower: spindle shaped (type C) in neuroid bundles (presumed schwannian derivation)
-
-
No cellular atypia nor junctional activity.
-
Junctional activity: melanocytes proliferation or dropping off restricted to basal portion.
-
D. Others:
-
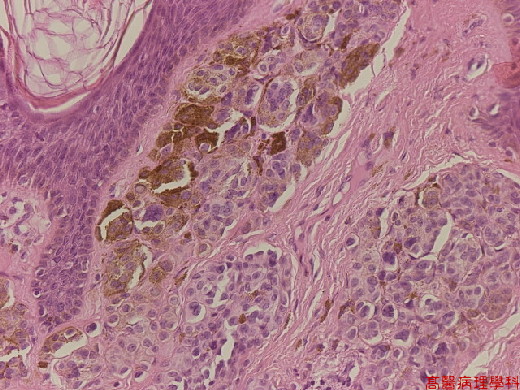
Melanocytes:
-
Neuroectodermal derived cells, located in the basal layer of skin, skin adnexae, & mucosal membranes.
-
Produce melanin & transfer through cytocrinia to adjacent epithelial cells.
-
Stains: silver, DOPA, S-100, vimentin.
-
Remove melanin pigments by potassium permanganate.
-
E. References:
-
Pathologic Basis of Disease. Ch27. p.1174-1176.
|
|
【 Fig. 135-1 (4X)】
|
|
【 Fig. 135-2 (10X)】
|
|
【 Fig. 135-3 (20X)】
|
|
【 Fig. 135-4 (40X)】
|
|
【 Fig. 135-5 (40X)】
|
|
【 Fig. 135-6 (40X)】
|
|
【 Fig. 135-7 (40X)】