《Slide 45.》Candidasis, Brain
A. Brief Descriptions:
-
The most common cause of human fungal infection.
-
Grow as yeast forms, tandem arrays of elongated forms without hyphae (psudohyphae).
-
Warm, moist surface; chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis; severe disseminated candidiasis.
B. Gross Findings:
略.
C. Micro Findings:
-
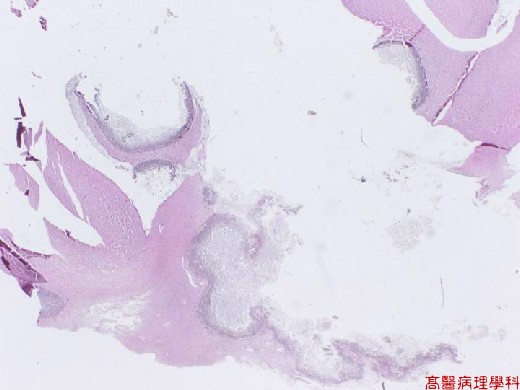
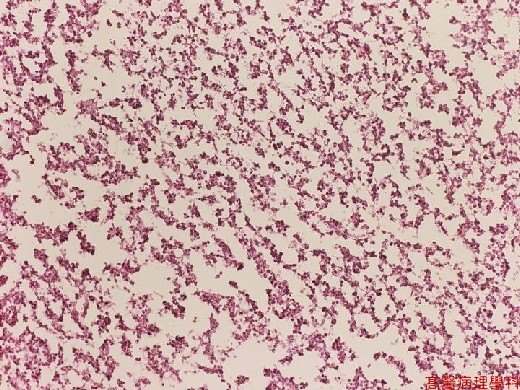
Abscess formation surrounded by a rim of gliosis.
-
Candida are seen among acute and chronic inflammatory cells near the abscess wall.
D. Others:
-
90% caused by Candida albicans.
-
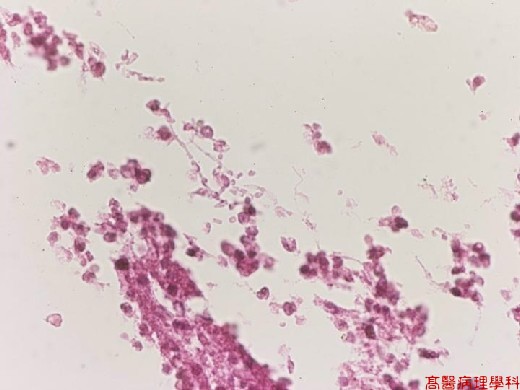
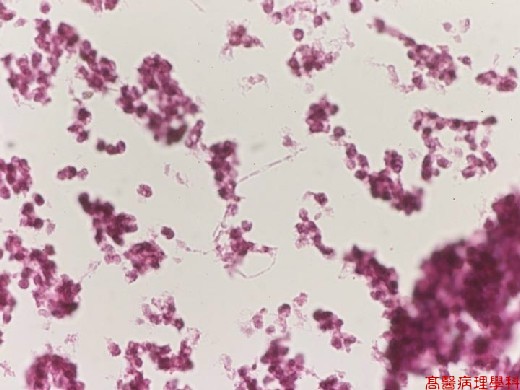
Ovoid yeast 3-4 m m, non - branching pseudohyphae and yeast joint end to end.
-
Developed when body defense mechanism is lowered; e.g. in immunodeficiency, immunosuppressant.
-
Candidemia is rare ; if disseminate , it would cause brain abscess, with local sign & can cause shock.
E. Reference:
-
Robbins Pathologic Basis of Disease, 6th ed. P.378-379.
|
|
【 Fig. 45-1 (LP)】 Several nodular structures within brain parenchyma.
|
|
【 Fig. 45-2 (LP)】The nodular strictures are composed of necrotic debris and inflammatory cells.
|
|
【 Fig. 45-3 (HP)】There are many yeast-form and filamentous-form fungal organisms within necrotic area.
|
|
【 Fig. 45-4 (HP)】The sprouting yeast-form fungi aligned in single array side-by-side resembling filemantous structure with hyphae (pseudohyphae).