《Slide 47.》Aspergillosis, Lung
A. Brief Descriptions:
-
Colonizing aspergillosis (aspergilloma) : proliferating fungal hyphae (fungus balls) form brownish masses lying free within the cavities.
-
Invasive aspergillosis.
B. Gross Findings:
略.
C. Micro Findings:
-
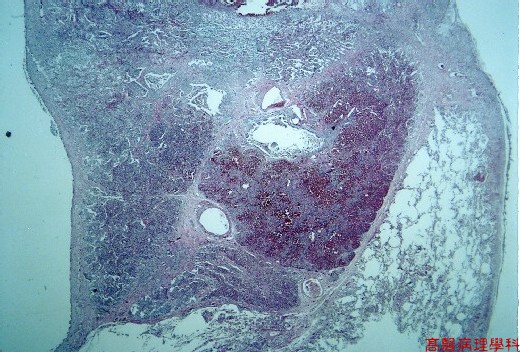
Accumination of fungal hyphae as a fungal ball in the destructed lung parenchyma, known as “ ball in hale ”.
-
Cavitaction with densely inflammatory infiltration.
-
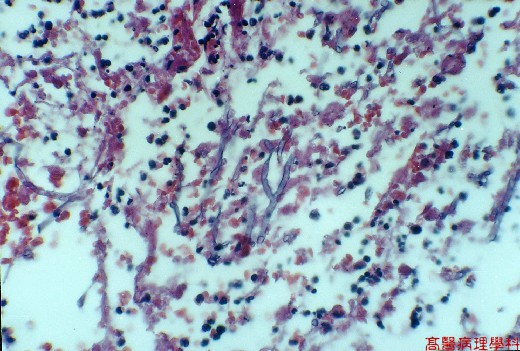
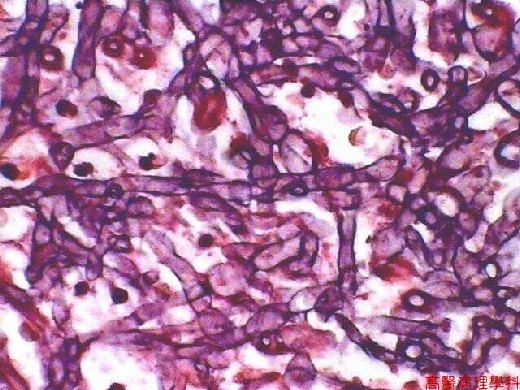
Fungal hyphae: narrow ( 3~5 m m ), separated, dichotomous, acute branching angle.
D. Others:
-
Caused by those of aspergillous genus: A. fumigatus, A. flavus, A. niger.
-
Fungal hyphae: narrow ( 3~5 m m ), separated, dichotomous, acute branching angle.
-
Special stains: GMS. or PASD.
-
Infection produces several different pattern of disease, depending on the degree of tissue reaction and host reaction.
-
In reading our slide :
-
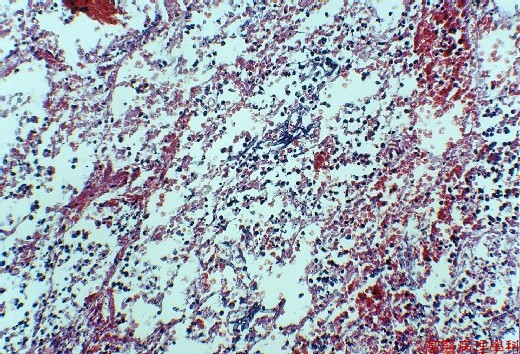
Hemorrhagic center surround by necrotic debris.
-
Fungal element can be found in necrotic debris.
|
type |
presentation |
test |
microscopy |
gross |
|
allergic |
asthma, adult |
skin test for aspergillous antigen |
collapse & consolidation of affected area eosinophil rich mucus goblet-cell hyperplasia |
Patchy Consolidation |
|
invasive |
in immuno- compromised patient |
|
invade bronchial wall & paren- chyma produce neutrophilic reaction invade blood vessel frequently characteristic branching (45° ) (A.niger, A. fumigatus) |
Hemorrhagic Center Surrounded by necrosis |
|
saprophytic |
aspergilloma in TB or bron-chioectasia |
X-ray |
fibrous wall cavity contain necrotic debris, fibrin, and mass of fungal element |
ball in hole |
E. Reference:
-
Robbins Pathologic Basis of Disease, 6th ed. P.379-380.
|
|
【 Fig. 47-1 (LP)】
|
|
【 Fig. 47-2 (LP)】
|
|
【 Fig. 47-3 (HP)】
|
|
【 Fig. 47-4 (HP)】