《Slide 38.》Dermoid cyst, Ovary
A. Brief Descriptions:
-
Benign cystic teratoma (dermoid cyst) is the most common ovarian neoplasm , comprising up to 25% or more of all ovarian tumors.
-
Contain various mature tissues derived from one or more of the embryonic germ layers : the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm.
B. Gross Findings:
-
Cystic mass containing thick sebaceous material and hairs.
-
The internal lining is smooth but frequently has a knob-like nodular protrusion in one.
-
Area (the “umbo”), in which cartilage, bone, and well-formed teeth may be present.
C. Micro Findings:
-
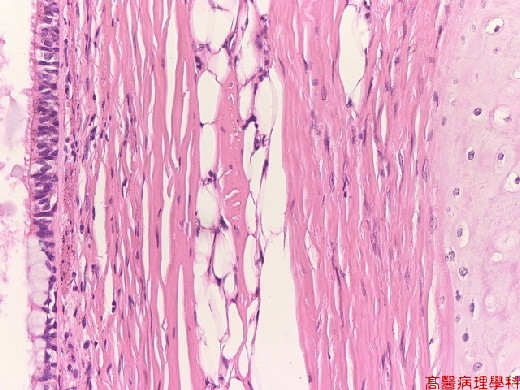
Skin element (dermal appendages, e.G. Hair follicles, sebaceous glands).
-
Endodermal element (respiratory and gastrointestinal epithelia).
-
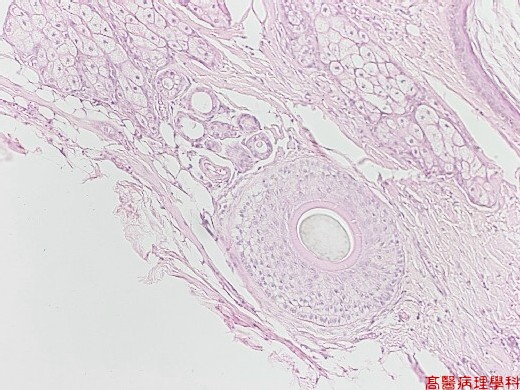
Mesodermal element (muscle, fat, cartilage).
-
Glial element.
D. Others:
-
Account for 15% of ovarian neoplasm, 10% bilateral.
E. Reference:
-
Robbins Pathologic Basis of Disease, 6th ed. P.1073-1075.
|
|
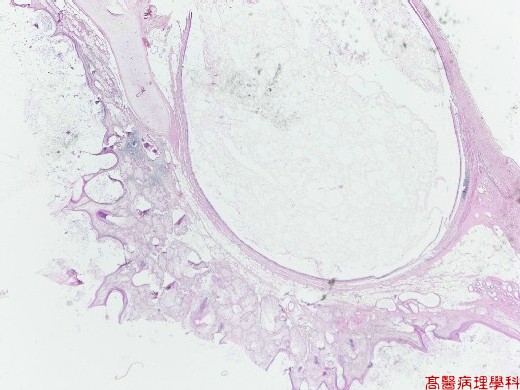
【 Fig. 38-1 (1X)】Cystic mass containing heterogeneous component.
|
|
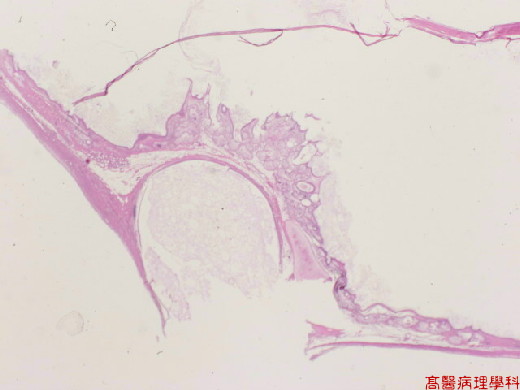
【 Fig. 38-2 (1X)】Dermoid component seen.
|
|
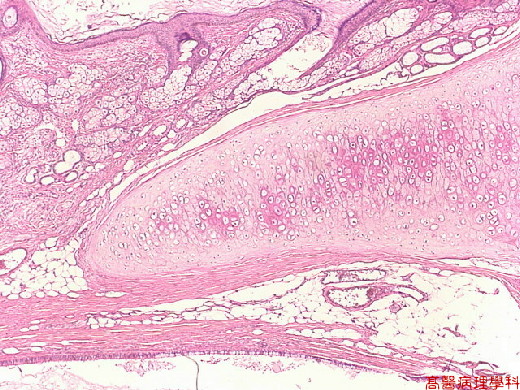
【 Fig. 38-3 (4X)】Sebaceous gland, adipose tissue, epithelial component, and cartilage are seen in this view.
|
|
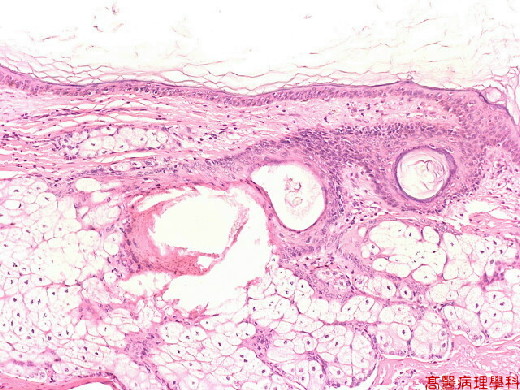
【 Fig. 38-4 (10X)】Skin element seen.
|
|
【 Fig. 38-5 (10X)】Ciliated epithelium seen in left view.
|
|
【 Fig. 38-6 (20X)】Skin element (dermal appendages, e.G. Hair follicles, sebaceous glands) seen in this view.