《Slide 51.》Atherosclerosis , Blood vessel
A. Brief Descriptions:
-
Atherosclerosis means hardening of the arteries.
-
Atherosclerosis primarily affects large to medium-sized muscular arteries and large elastic arteries, marked by elevated focal intimal fibro-fatty plaques principally in the abdominal aorta or coronary arteries.
-
Major risk factors : hypertension, diabetes mellitus, smoking , hypercholesterolemia.
B. Gross Findings:
-
Fatty streak :
infiltration of lipids into certain intimal cells,multiple yellow、flat spots coalescece into elongated streaks → fatty streak( precursors of atherosclerosis ). -
Atheromatous plaques :
progressive accumulation of lipids causing tissue degeneration and fibrosis → focal intimal fibrolipid plaque. -
Complicated atheroma :
internal hemorrhage, calcification, ulceration and thrombus formation → complicated atheroma.
C. Micro Findings:
-
Fatty streak : intimal collections of lipid-laden macrophages and smooth muscle cells.
-
Atheromatous plaque(atheroma): Fibrous cap +Necrotic center.
-
Superficial fibrous cap: smooth muscle cells、Lipid-laden macrophage ( Foam cells )、macrophage、lymphocytes、collagen、elastin、proteoglycans.
-
Central necrotic core: dead cells、lipid、cholesterol clefts、lipid-laden foamy cells、calcification.
-
Around the plaque : neovascularization may be seen.
-
D. Others:
略.
E. Reference:
-
Robbins Pathologic Basis of Disease, 6th ed. P.498-510.
|
|
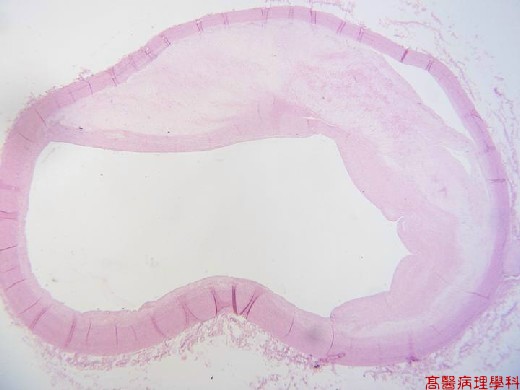
【 Fig. 51-1 (LP)】Atherosclerotic change of aorta with thickened wall and decreased lumen .
|
|
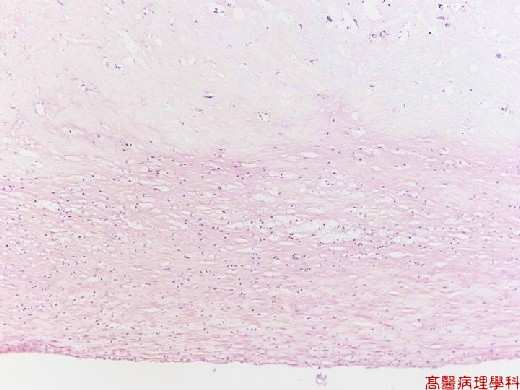
【 Fig. 51-2 (LP)】Large areas of central necrotic zone (right) with cholesterol and fibrous deposits and few cells, while near the lumen, it shows more cellular zone with proliferation of smooth muscle cells and macrophages.
|
|
【 Fig. 51-3 (LP)】The central necrotic zone (upper) and the cellular zone (lower).
|
|
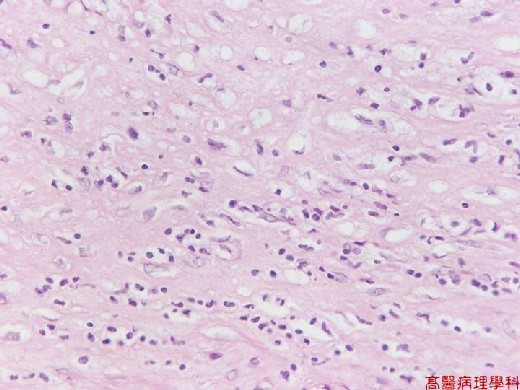
【 Fig. 51-4 (HP)】The cellular zone with proliferation of smooth muscle cells and macrophages.