《Slide 83.》Squamous cell carcinoma in situ, Cervix
A. Brief Descriptions:
-
Human papilloma virus (HPV) is currently considered and important factor in cervical oncogenesis.
-
Koilocytic atypia: nuclear atypia and perinuclear vacuolization → viral “cytopathic” effect; in the upper and middle lining squamous epithelium.
-
Classification:
-
Dysplasia: mild, moderate and severe.
-
Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN): CIN I, II, III.
-
Squamous intraepithelial lesion (SIL): low-grade and high-grade.
B. Gross Findings:
No significant lesion.
C. Micro Findings:
-
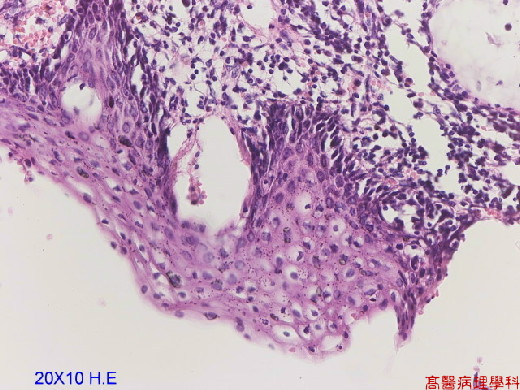
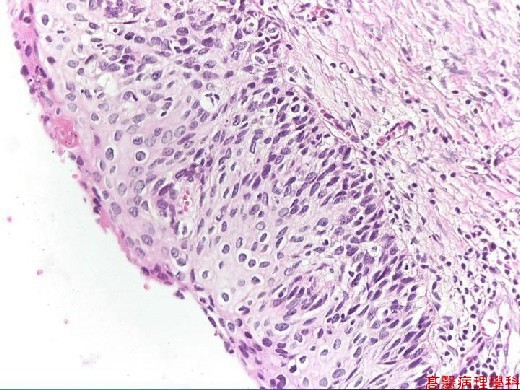
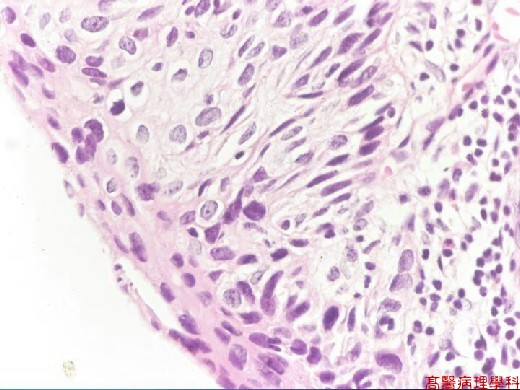
Full-thickness dysplasia without any differentiation: atypical cells with hyperchromatism, altered polarity, and irregular nuclei in the entire thickness of squamous epithelium.
-
Basement membrane is intact. No stromal invasion.
D. Others:
-
Compare with slide 185.
E. Reference:
-
Robbins Pathologic Basis of Disease, 6th ed. P.1049-1051.
|
|
【 Fig. 83-1 (LP)】Full-thickness dysplasia of squamous epithelium.
|
|
【 Fig. 83-2 (LP)】Altered polarity of the epithelium without stromal invasion.
|
|
【 Fig. 83-3 (HP)】Severely dysplastic keratinocytes with hyperchromatic and pleomorphic nuclei.