|
|
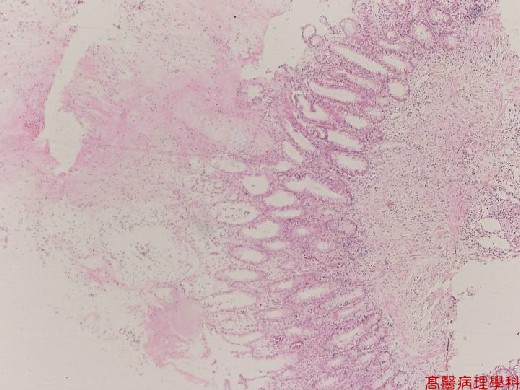
【 Fig. 56-1 (LP)】Superficial erosion of the mucosa and an adherent "pseudomembrane" of fibrin, mucus, and inflammatory debris.
|
|
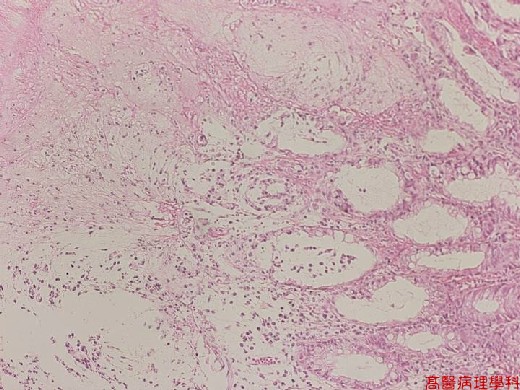
【 Fig. 56-2 (LP)】Superficial crypts are distended and damaged with inflammatory infiltration.
|
|
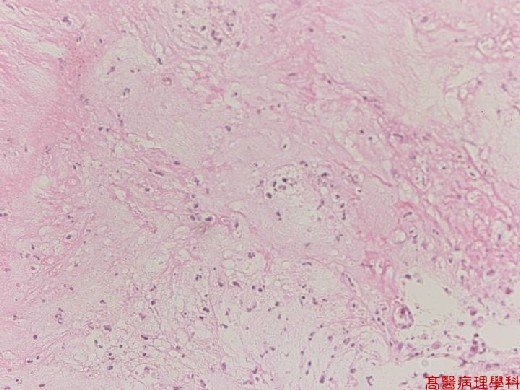
【 Fig. 56-3 (HP)】"Pseudomembrane" contains amorphous, eosinophilic, fibrin exudate with cellular debris and inflammatory infiltrates.